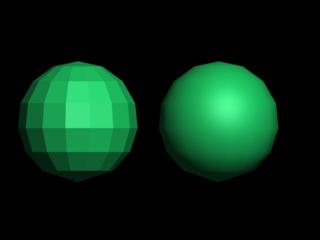
Objects are modeled in 3D using curves (splines) or polygons.
Rendering is the process of taking a 3D object viewed from some position and drawing it onto a 2D screen/window. The "drawing" is done by projecting the polygons that make up a surface onto a 2D surface. Thus, all objects must be describable using polygons. Splines are converted to polygons by specifying a desired resolution. The higher the resolution, the smoother the resulting polygon surface looks.
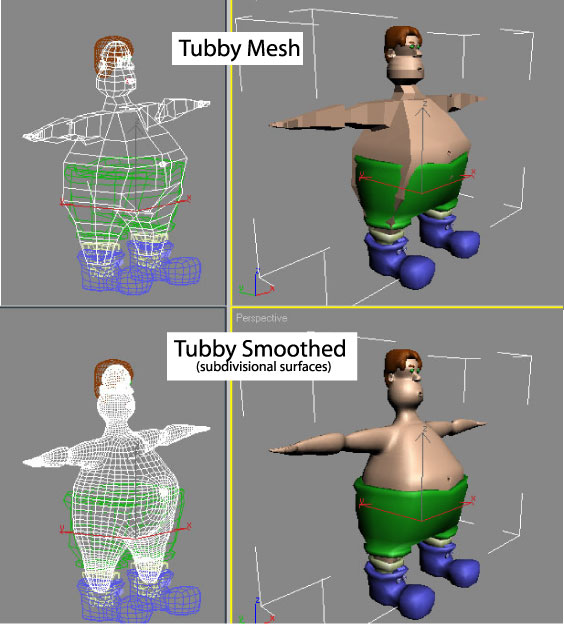
Any polygonal object (including those generated from splines) is not prefectly smooth, but is made up of many little flat surfaces. The surface can be given the appearance of being smooth using shading techniques such as averaging the directions of adjacent polygons (e.g. gouraud or phone shading). The surface can also be made more smooth using subdivision surfaces, a technique that adds (automatically by the computer) more polygons in a way that smooths out the surface.

There are different ways that a modeler can generate the polygons:
Procedural: An object is described using a mathematical equation. The modeler just needs to specify a few parameters required in the equation. The computer uses this equation to generate sets of points (vertices) and edges (pairs of vertices) and polygons (sets of edges). This works well for simple shapes such as a sphere, ellipse, and torus. However, it is impractical for most of the shapes we want to model.
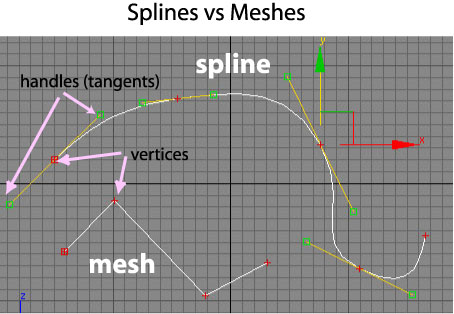
Mesh Modeling: The modeler specifies a set of vertices, edges, and polygons. For complex shapes this can be very time consuming especially for objects that are very organic in shape (i.e. not a lot of straight lines) because every curve requires many points to specify. However, the recent introduction of subdivisional surfaces has made mesh modeling more practical for these types of shapes.
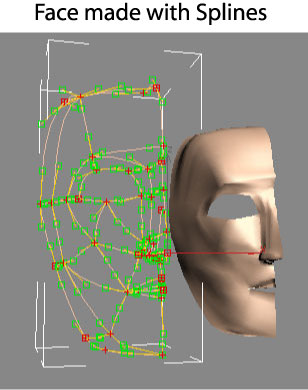
Spline Modeling: When using splines, the modeler must specify vertices and handles that mathematically define a curve. The vertices lie on the curve and the handles define tangents to the curve at the vertices (see picture below). The computer uses the spline equations to generate the needed points required for the polygon mesh. Because a mathematical equation is used to describe the curve, the computer can draw the curve with as much precision as desired without the user having to add additional points. For those interested in the mathematical details, look here.
NURBS (non-uniform rational b-splines): These are similar to splines in that they are smooth curves mathematically derived from sets of points. They have definite advantages of splines in that they can represent a wider range of shapes and provide more degrees of freedom. However, they are also more difficult to work with. For those interested in the mathematical details, look here.
[Top] | [Home] |